The most prevalent form of diabetes, type 2, can be halted with lifestyle adjustments. If you already have type 2 diabetes due to being overweight or obese, having high cholesterol, or having a family history of the disease, prevention is crucial.

A change in lifestyle can stop or delay the beginning of the disease if you have prediabetes, which is elevated blood sugar that is not yet diagnosed as diabetes.
Making a few little lifestyle adjustments today may help you prevent potential major health issues associated with diabetes, such as damage to your nerves, kidneys, and heart. Starting is never too late.
1. Reduce excess weight
Obesity lowers the risk of developing diabetes. People in one significant trial who lost roughly 7% of their body weight by dietary and exercise improvements saw a nearly 60% reduction in their chance of acquiring diabetes.
To stop the disease from progressing, the American Diabetes Association advises prediabetic individuals to lose between 7% and 10% of their body weight. Greater advantages will result from further weight loss.
Based on your current body weight, choose a weight loss target. To lose one to two pounds every week, for example, discuss acceptable short-term objectives and expectations with your doctor.
2. Increase physical activity
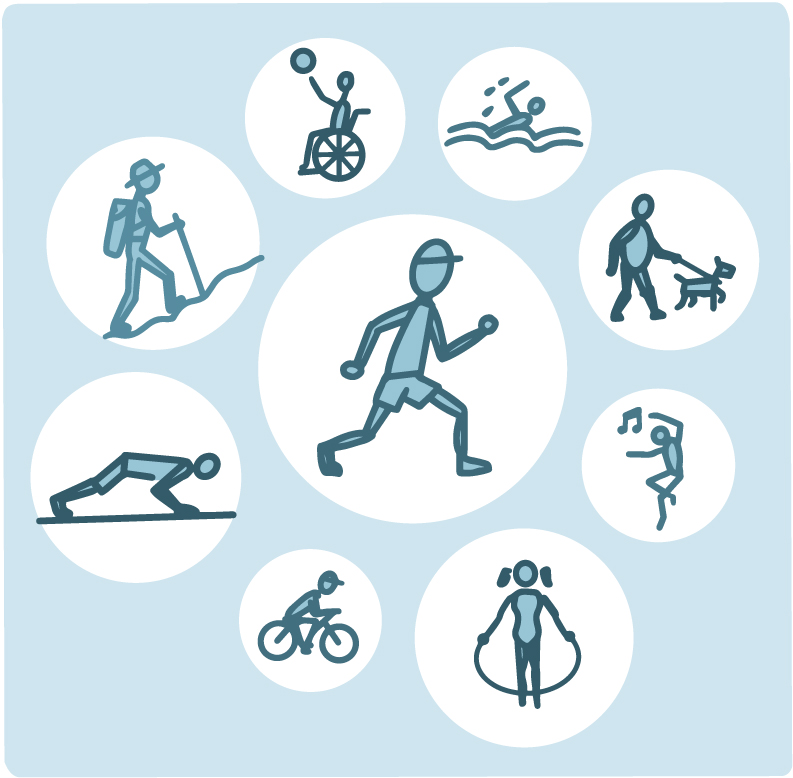

Regular exercise has a variety of advantages. Exercise benefits include:
- reduce weight
- Reduce your sugar levels.
- Increasing your sensitivity to insulin will help you maintain a normal range for your blood sugar.
Most persons set the following objectives to encourage weight loss and keep a healthy weight:
Aerobic activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate to strenuous aerobic activity each week, which should include at least 30 minutes of brisk walking, swimming, bicycling, or running.
Resistance workout. Your strength, balance, and capacity to lead an active life are all improved by resistance training, which you should do at least 2 to 3 times per week. Yoga, callisthenics, and weightlifting are all forms of resistance exercise.
Limited inactivity. Long periods of inactivity, such working at a computer, can be broken up to assist manage blood sugar levels. Every 30 minutes, spend a few minutes standing up, moving around, or engaging in some light exercise.
3. Consume wholesome plant foods
Plants supply your food with vitamins, minerals, and carbs. Sugars, starches, and fibre are all types of carbohydrates. They are the sources of energy for your body. Roughage and bulk are other terms for dietary fibre, which is the portion of plant foods that your body cannot digest or absorb.
Foods high in fibre encourage weight loss and reduce the incidence of diabetes. Consume a range of wholesome, high-fiber foods, such as:
- fruits from trees, such as tomatoes, peppers, and other berries
- Non-starchy vegetables include broccoli, cauliflower, and leafy greens
- Beans, chickpeas, and lentils are examples of legumes.
- Whole grains, such as quinoa, whole-grain rice, whole-grain oats, and whole-wheat pasta and bread
Among the advantages of fibre are:
- reducing blood sugar levels and slowed sugar absorption
- preventing the digestion of dietary cholesterol and lipids
- Controlling other risk factors, such as blood pressure and inflammation, that have an impact on heart health
- assisting you in eating less by being more full and energetic than foods low in fibre
- Avoid “bad carbs” like white bread and pastries, pasta made from white flour, fruit juices and processed foods that are heavy in sugar or high-fructose corn syrup but low in fibre or nutrients.
4. Consume good fats.
Since fatty meals are heavy in calories, they should only be consumed occasionally. Your diet should contain a range of foods with unsaturated fats, also referred to as “good fats,” to aid in weight loss and management.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are both types of unsaturated fats, support normal blood cholesterol levels as well as heart and vascular health. Good fat sources include:
- oils from cottonseed, safflower, olive, sunflower, and canola
- Almonds, peanuts, flaxseed, and pumpkin seeds are a few examples of nuts and seeds.
- Salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, and cod are examples of fatty fish.
Dairy products and meats include saturated fats, also known as “bad fats.” You should only eat a tiny amount of these. By consuming low-fat dairy products, lean chicken, and pork, you can reduce your intake of saturated fats.
5. Avoid fad diets and opt for healthy alternatives.

Several fad diets, including the paleo, keto, and glycemic index diets, may aid in weight loss. However, there is little information available regarding the long-term advantages of these diets or their use in preventing diabetes.
Your eating objective should be to reduce weight and then go forward maintaining a healthier weight. So, making healthy food choices requires a plan that you can stick to as a lifelong habit. Over time, you might benefit from making healthy options that incorporate some of your own gastronomic preferences and cultural customs.
Divide your plate into smaller servings as one easy way to aid in optimal food selection and consumption. Your plate’s three sections that encourage healthy eating are:
- Fruit and no vegetables make up half.
- Whole grains make up one-quarter.
- 25%: foods high in protein, like lean meats, fish, and legumes
When to visit the doctor
All persons age 45 and over, as well as the following groups, should undergo routine testing for type 2 diabetes with diagnostic tests:
- individuals under 45 who are overweight or obese and have one or more diabetes risk factors
- Pregnant women with gestational diabetes
- those with prediabetes who have received a diagnosis
- Children who are overweight or obese, have a history of type 2 diabetes in their family, or who otherwise have a risk
Tell your doctor about your worries regarding diabetes prevention. He or she will be appreciative of your efforts to avoid diabetes and perhaps provide more recommendations in light of your medical background or other circumstances.
Also read
The Tomato Crisis Has Not Stopped This Farmer From Pune From Turning A Profit Of Over 2 Crore