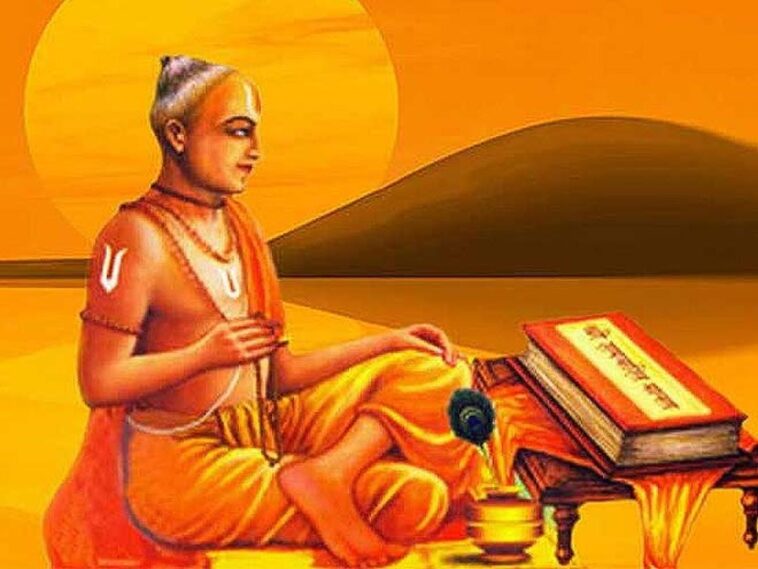
Tulsidas wrote the epic Ramcharitmanas in the Awadhi language in the 16th century, adapting the original Ramayana stories with new generations in mind.
The Ramcharitmanas is neither a word-for-word transcription nor a condensed version of the Valmiki Ramayana. Ramcharitmanas contains elements from numerous other Ramayanas written in Sanskrit and various Indian dialects, as well as tales from the Puranas.
A Brief Description of Tulsidas and His Ramcharitmanas
Tulsidas was born on the Saptami Tithi of Shukla Paksha in the month of Shravan (July or August) in Rajapur, Uttar Pradesh, on the banks of the Yamuna. (also known as Chitrakoot).
His paternal grandparents were named Atmaram Shukla Dubey and Hulsi Dubey. According to legend, Tulsidas spent one year in his mother’s bosom.
Tulsidas was born with 32 teeth; he did not weep and instead spoke the name Ram, so his childhood name was Rambol.
Tulsidas refers to the epic Ramcharitmanas as Rama’s story, which was stored in Shiva’s mind (Manasa) and then narrated to Shiva’s wife, Devi Parvati.
Tulsidas asserts that he learned the tale from his guru, Narharidas. Tulsidas was a naive child, and the narrative was preserved in his mind (Manasa) for a considerable amount of time before he penned Ramcharitmanas.
Consequently, the epic is also known as Tulsikrit Ramayana. (The Ramayana composed by Tulsidas). The Ramcharitmanas is a vernacular literary masterpiece.
The Shri Ramcharitmanas
1. The Ramayana and the Ramcharitmanas are dissimilar.
Ramcharitmanas and Ramayana are two distinct Sanskrit and Awadhi versions of the Rama narrative. There are differences between them in terms of poetic technique, composition, and religious significance, among others.
Sage Valmiki is the author of Ramayana. It is regarded as Adi Kavya, or the first book of elaborate poetry. The Ramcharitamanas is based on the original composition of Valmiki. The great Awadhi poet Goswami Tulsi Das penned it.
Tulsidas compared the Seven Kandas or chapters to the seven steps that lead to Lake Manasa. Popular belief holds that a bath in Manasarovar, located near Mount Kailash, cleanses the psyche and body of all impurities.
2. Ramcharitmanas as the Bible of North India
It is not an exaggeration to state that Western scholars consider the Ramacharitmanas to be the North Indian Bible. This is because the work contains numerous spiritual and religious ideas. The patriarch of India, Mahatma Gandhi, frequently considered Tulsidas’ Ramayana to be more spiritual than Valmiki’s.
3. Seven Ramcharitmanas Kandas
Tulsidas wrote the work in seven Kandas, and they are termed Bala Kanda, Ayodhya Kanda, Aranya Kanda, Kishkindakand, Sundar Kanda, Lanka Kanda, and Uttar Kanda. The primary distinction between the Valmiki Ramayana and the Ramacharitmanas is that Tulsidas titled the sixth chapter Lanka Kanda rather than Yuddh Kanda.
4. The Composition of Ramcharitmanas
Ram appears 1,443 times throughout the Ramcharitmanas. The term Sita appears 147 times in Ramcharitmanas, while Janaki appears 69 times. Baidehi is mentioned 51 times, while Temple is mentioned 35 times.
Similarly, there are 27 verses in the Ramcharitmanas, 4608 in the Chopai, and 1074 in the Doha of the Ramcharitmanas. This epic’s shortest chapter is Kishkindhakand, while the longest is Balakanda.
When he composed Ramcharitmanas, Tulsidas was 77 years old. Tulsidas began writing it in 1574 and completed it two years, seven months, and twenty-six days later in 1576. Also considered an incarnation of Maharishi Valmiki is Tulsidas. In a dream, Lord Shiva inspired him to write the Ramcharitmanas.
5. Ramcharitmanas Details
According to Ramcharitmanas, Pushpak Vimana traveled at a pace of 400 miles per hour, the war between Rama Team and Ravana Team lasted 87 days, and the war between Ram and Ravan lasted 32 days.
Similarly, it took five days to construct a bridge across the ocean to reach Sri Lanka. Lord Ram stayed in Lanka for 111 days, and Sita stayed in Lanka for 435 days. Sarama served Sita in Ashok Vatika while she was in Lanka. Sarama is the daughter of the monarch of the Gandharvas, Shailush, and the consort of the king of the asuras, Vibhishana.
Also read: Ram Navami 2023
6. The Story of Shurpanakha
Vidyujjihi was the spouse of Shurpanakha, Ravana’s only sister. For some reason, Ravana killed Vidyujjihi. She then mentally cursed Ravana that he would perish because of a woman.
After becoming a widow, Shurparnakha became autocratic, so Lakshman severed her nose on the orders of Shri Ramchandra.
7. The truth of Ravana
Ravana was the monarch of Lanka, but Kuver, Ravana’s half-brother, was the genuine ruler of Lanka. According to Ramcharitmanas, Kuver was also a devotee of Shiva; Shiva, delighted with Kuver’s penance, bestowed upon him Lanka, which Ravana would later conquer in the course of their conflict.
Ravana was a devoted follower of Lord Shiva. Ravana severed his cranium and offered it to Shiva as a sign of his penance. Lord Shiva, moved by Ravana’s devotion, granted Ravana ten heads; hence, Ravana is also known as Dashanan. (the one with ten heads).
8. Sri Ram had a sister as well.
Rama, Lakshmana, Bharata, and Shatrughan were four siblings, and Shanta was their older sister. Shanta was the eldest daughter of King Dasharatha and Kaushalya, but King Dasharatha gave her to King Rompad of Angadesh when she was a child for unknown reasons.
Shanta was reared by King Rompad and his childless wife Varshini, who jokingly requested a child during a visit to Ayodhya. Shanta became the heiress of Angadesh when King Dasharatha kept his word.
9. The Story of Meghnath
Meghnad is featured in the Ramcharitmanas. He was the son of King Ravana and Mandodari. His name means “one whose speech resembled thunder,” and he was renowned for his exceptional combat abilities. Meghnad was the most formidable warrior in Lanka’s army, and his valor was dreaded. He even defeated Indra, the monarch of the gods, to earn the name Indrajit.
He was cursed to be slain by the individual who hadn’t slept for 14 years. Since Lakshman had not slept for fourteen years, he is also known as Gudakesh. Meghnath was therefore slain by Lakshman.
10. Tulsidas Vision
In a number of his works, Tulsidas claims to have had direct visions (darshan) of Lord Hanuman, Lord Rama-Lakshman, and Shiva-Parvati.
During his travels, Tulsidas encountered a devotee in Kashi who provided him with Hanuman’s address. After having seen Hanuman, he was granted a vision of Lord Rama. However, when Lord Rama granted Tulsidas darshan, he was unable to recognize him.
Lord Rama visited Tulsidas once more on the day of Mauni Amavasya, and this time Hanuman assisted him identify Lord Rama.
Ramcharitmanas in Contemporary Times
During his commencement address at Nalanda Open University, the former education minister of Bihar, Chandra Shekhar, asserted that the Ramcharitmanas can propagate hatred in society. He stated that it is one of the religious texts containing questionable statements about Dalits and Backward people. Despite the fact that Gita Press of Gorakhpur asserts that the Ramcharitmas is a sacred text that should not be replaced, it has been selling large quantities of the Hindu epic. (more than 7 crores pieces).
Both the Ramayana and the Ramcharitmanas have achieved great significance in the lives of Hindus worldwide. The theory of karma, reincarnation, Advaita-Vedanta, brahmana, jiva, Maya, and Isvara is the most significant aspect of the Ramcharitmans. Ramcharitmanas spread the story of Ram to every home.