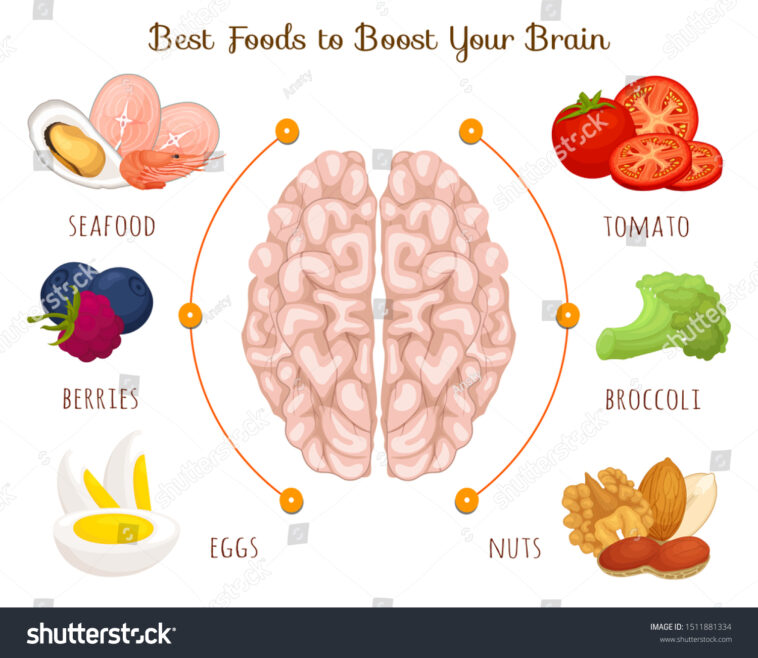
The consumption of brain-friendly foods has been linked to improved memory and focus, as well as general brain health.
Your brain is a really significant organ.
Your brain is your body’s command centre, regulating everything from your heart rate and respiration to your ability to move, feel, and think.
This is why maintaining optimal brain health through diet is so important.
1. Fatty fish

Fatty fish is frequently mentioned as one of the best nutrients for the brain.
Salmon, trout, albacore tuna, herring, and sardines are all examples of fatty fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids (1Trustworthy Source).
Half of the fat in your brain is omega-3 fatty acids (2 Trusted Source), and that fat makes up about 60% of your brain.
Omega-3s have a crucial role in the development of new brain cells and the maintenance of existing ones (2, 3).
There are a number of other cognitive benefits to taking omega-3s.
One possible benefit is that they mitigate the effects of ageing on the brain and reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease (4, 5, 6, 7).
On the other hand, research suggests that a deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to cognitive decline and depression (3Trustworthy Source, 8Trustworthy Source).
In general, there appears to be beneficial health effects from eating fish.
Regular fish eaters have been linked to an increase in brain volume, according to the literature. Most of the nerve cells responsible for making decisions, remembering things, and feeling emotions are located in the grey matter (9 Trusted Source).
In general, eating fatty fish is a great thing to do for your brain.
2. Coffee

For those of you who look forward to your morning cup of joe, the news that it has health benefits will come as welcome news.
Caffeine and antioxidants, two of coffee’s key components, are good for your brain.
Numerous studies have shown that caffeine, which is present in coffee, has beneficial impacts on cognitive function.
Enhanced vigilance. Caffeine prevents the release of adenosine, a chemical messenger that induces sleepiness, in the brain (11Trustworthy Source, 12Trustworthy Source).
Elevated spirits. There is some evidence that caffeine can increase the levels of “feel-good” neurotransmitters like dopamine (13Trustworthy Source).
Enhanced ability to focus. Caffeine has been shown to increase focus and alertness temporarily, according to one study (14Trustworthy Source).
There is some evidence that long-term coffee use can protect against the onset of neurodegenerative disorders including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. Adults who drank three to four cups every day significantly reduced their chance of developing certain diseases (10 Trusted Sources, 15 Trusted Sources).
The high levels of antioxidants in coffee could be responsible for this, at the very least in part.
3. Blueberries

There are many ways in which blueberries can improve your health, including your brain.
The anthocyanins found in blueberries and other darkly coloured berries have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits (17Trustworthy Source).
Both oxidative stress and inflammation, which antioxidants work to prevent, have been linked to accelerated brain ageing and the development of neurodegenerative disorders (18).
A number of blueberry antioxidants have been shown to concentrate in the brain, where they promote better communication between nerve cells (17Trustworthy Sources, 19Trustworthy Sources).
One meta-analysis of 11 trials found that eating blueberries helped enhance memory and other cognitive processes in both young and old people (20).
You can eat them as is, sprinkle them on your cereal, blend them into a smoothie, or do any number of other things.
4. Turmeric
Recently, there has been much talk about turmeric.
This bright yellow spice is a vital component of curry powder and has been shown to have positive effects on cognitive function.
The key element in turmeric, called curcumin, has been found to penetrate the brain and aid cells there (21Trustworthy Source).
There is evidence linking this powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory substance to the improvement of the following cognitive functions:
Potentially good for the brain’s memory. Alzheimer’s patients taking curcumin may see an improvement in their memory. The amyloid plaques that are characteristic of this condition may also be removed with this treatment (21Trustworthy Source, 22Trustworthy Source).
helps with depression. Curcumin increases the feel-good chemicals serotonin and dopamine. When combined with conventional therapy for depression, curcumin has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety in at least one review (23Trustworthy Source, 24Trustworthy Source).
It promotes the development of new nerve cells in the brain. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a sort of growth hormone that promotes the proliferation of brain cells, and curcumin increases its levels. More research is needed, although it may help slow down cognitive deterioration with ageing (25Trustworthy Source, 26Trustworthy Source).
Remember that most studies utilise 500–2,000 milligramme (mg) daily doses of curcumin supplementation, which is far more curcumin than most people generally consume when using turmeric as a spice. This is because the curcumin content of turmeric is so low (approximately 3-6%, according to 27Reliable Source).
To get the benefits seen in these trials, it may be necessary to take a curcumin supplement under a doctor’s supervision, even though adding turmeric to your food may be beneficial.
5. Broccoli
Strong plant components, such as antioxidants, are abundant in broccoli (28Trustworthy Source).
More than 100 percent of the daily value for vitamin K can be found in just 1 cup (160 grammes) of cooked broccoli (29Trustworthy Source).
The formation of sphingolipids, a type of fat that is highly concentrated in brain cells (30Trustworthy Source), requires this fat-soluble vitamin.
Also Read: Why Love Marriage Is Better Than Arranged Marriage
A higher vitamin K consumption has been linked in a few studies (31Trustworthy Source, 32Trustworthy Source) to improved memory and cognitive state in older persons.
Broccoli’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties come from a combination of substances beyond vitamin K (33Trustworthy Source).
6. Pumpkin seeds
The antioxidants included in pumpkin seeds can prevent cell damage caused by free radicals (34).
Magnesium, iron, zinc, and copper are also abundant in them (35Trustworthy Sources).
All of these vitamins and minerals are essential for proper brain function:
Zinc. The transmission of nerve impulses relies on this component. Deficits in zinc have been associated with a wide range of neurological disorders (36Trustworthy Source, 37Trustworthy Source, 38Trustworthy Source), including Alzheimer’s disease, depression, and Parkinson’s disease.
Magnesium. You can’t learn or remember anything without magnesium. Migraines, depression, and epilepsy are just some of the neurological disorders that have been associated to low magnesium levels (39Reliable Source, 40Reliable Source).
Copper. Copper aids in the regulation of nerve messages in your brain. Increased vulnerability to neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s is associated with abnormal copper levels (41Trustworthy Source, 42Trustworthy Source).
Iron. Low iron levels are associated with poor cognitive performance (43Reliable Source).
These micronutrients, rather than pumpkin seeds, are the primary focus of the studies. However, since pumpkin seeds are rich in these micronutrients, eating more pumpkin seeds may help you achieve your health goals.
7. Dark chocolate
Flavonoids, caffeine, and antioxidants are just some of the brain-boosting components found in dark chocolate and cocoa powder.
Dark chocolate is defined as having a cocoa content of 70% or above. Milk chocolate, which typically contains only between 10–50% cocoa, does not provide these advantages.
Antioxidant flavonoids are found in many plants.
Flavonoids in chocolate congregate in memory and learning hubs of the brain. These chemicals have been studied for their potential to improve memory and prevent cognitive decline with ageing (44, 45).Reliable Reference, 46)Reliable Sourcing.
Indeed, several research (47Trustworthy Source, 48Trustworthy Source, 49Trustworthy Source) corroborate this.
One study involving more than 900 people found that those who consumed chocolate on a regular basis outperformed those who rarely did so across a range of mental activities, including memory-related ones (50 Trusted Source).
Studies have shown that eating chocolate can improve your mood.
Positive emotions were observed to be higher in the chocolate eaters compared to the cracker eaters (51Trustworthy Source).
Whether this is due to chemical substances in chocolate or just the pleasant taste remains unclear
8. Nuts
Eating nuts has been proven to boost heart-health markers (52Trustworthy Source, 53Reliable Source), and a healthy heart has been related to a healthy brain.
Regular nut consumption may be associated with a reduced risk of cognitive impairment in older persons, according to one study (54Reliable Source).
The memory of women who consumed nuts on a regular basis for at least three years outperformed that of women who did not (55Reliable Source), according to a study conducted in 2014.
Nuts are good for you for many reasons, and it’s possible that nutrients like healthy fats, antioxidants, and vitamin E are to thank (56Trustworthy Source, 57Trustworthy Source).
Mental decline can be slowed by taking vitamin E because it prevents cell damage from free radicals (58Trustworthy Source, 59Trustworthy Source).
Walnuts, like other nuts, are excellent for your brain, but they may offer an advantage due to the anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids they provide (57Trustworthy Source).
9. Oranges
One medium orange provides about all of the vitamin C you need for the day (60 Trusted Source).
Since vitamin C is a major element in avoiding mental deterioration (61Trustworthy Source), this is crucial for brain health.
One study found that people with higher blood levels of vitamin C performed better on concentration, memory, attention, and decision-making activities (62 Trusted Source).
Brain cells can be damaged by free radicals, but vitamin C can help fight them off. Vitamin C also helps maintain brain function in old age, and it may reduce the risk of developing mental health issues like depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and dementia (63Reliable Source).
Bell peppers, guava, kiwi, tomatoes, and strawberries are also excellent sources of vitamin C.
10. Eggs
Vitamins B6 and B12, folate, and choline are all important for brain health, and eggs are a rich source of all four (64).
Choline is a crucial vitamin because it is used by the body to produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in maintaining mood and memory (65, 66, 67).
Higher choline intake has been associated to enhanced memory and cognitive performance in two older research (68Trustworthy Source, 69Trustworthy Source).
However, choline is often lacking in people’s diets.
The yolk of an egg is one of the best places to receive choline because of its high concentration.
The recommended daily allowance for choline is 425 mg for most women and 550 mg for most men (Trusted Source65), while one egg yolk contains 112 mg.
In addition, the B vitamins in eggs have multiple roles in maintaining brain health.
The amino acid homocysteine has been related to dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, and by reducing its levels, these supplements may help prevent the onset of mental decline in the elderly (70Trustworthy Source, 71Trustworthy Source).
Folate and B12 deficiencies are also associated with depression (72 Trusted Source).
The cognitive deterioration associated with ageing has been shown to be mitigated by taking folic acid supplements (73Trustworthy Source, 74Trustworthy Source), and folic acid deficiency is common in the elderly with dementia.
The synthesis of brain chemicals and the regulation of brain sugar levels both rely on vitamin B12 (72Trustworthy Source).
However, there is scant evidence linking egg consumption with improved cognitive function. However, there is evidence that some nutrients in eggs can improve cognitive function.
The bottom line
There are many options for keeping your brain healthy.
Brain-protecting antioxidants can be found in foods like the ones on this list as well as others like tea and coffee.
Nuts and eggs, for example, are packed with nutrients that are good for the brain and can help you remember things.
By include these items in your diet, you can improve your mental state and increase your energy, focus, and mood.
There’s just one item. Try this today: it’s just as vital to avoid eating foods that can harm your brain as it is to eat these brain-boosting foods. Here is a list of the seven foods you should limit or avoid altogether because of their negative effects on your brain.