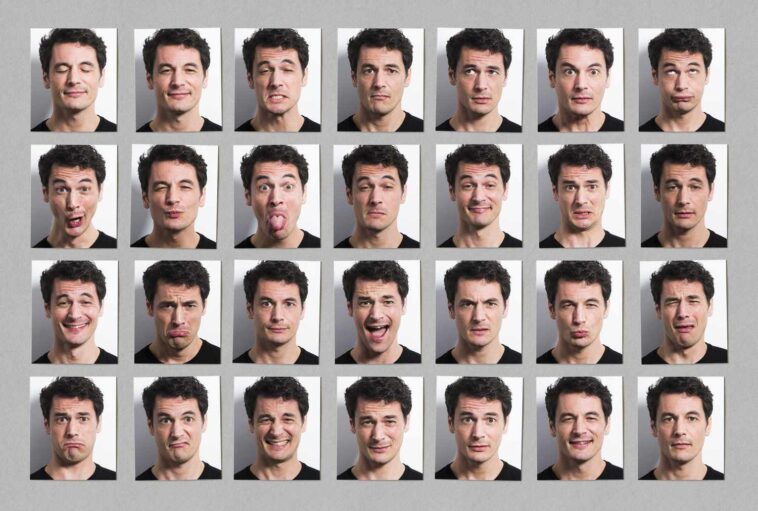
Different theories of emotion attempt to provide light on the meaning, origin, and consequence of the range of human emotions. Emotions have a tremendous impact on how we act. Extreme feelings can make you do things you wouldn’t typically do or keep you from engaging in pleasurable activities.
What use do emotions serve? Why do they occur? Scientists, philosophers, and psychologists have all put forth theories of emotion to try and explain the mechanism(s) and motivation(s) underlying human emotional experiences.
Types of Theories of Emotion
Physiological theories
Emotions, according to certain physiological theories, are caused by a chain reaction inside the body.
Neurological theories
Emotions, according to neurobiological theories, are caused by mental processes.
Cognitive theories
Emotions, according to cognitive theories, are formed mostly as a result of one’s own ideas and other mental activities.
The evolutionary theory, the James-Lange theory, the Cannon-Bard theory, the Schachter-Singer theory, the cognitive appraisal theory, and the facial-feedback theory are just six of the many theories of emotion offered by psychologists.
Evolutionary Theory of Emotion
Charles Darwin claimed that feelings evolved because they served a functional purpose in the survival and reproduction of humans and other animals. People are motivated to find partners and have children by their need to love and be loved. When threatened, people’s natural responses are to either fight back or run away.
The James-Lange Theory of Emotion
One well-known example of a physiological theory of emotion is the James-Lange theory. The James-Lange hypothesis of emotion, independently postulated by psychologist William James and physiologist Carl Lange, holds that emotions are generated by the body in response to external stimuli.1
The Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
The Cannon-Bard hypothesis of emotion is another well-known physiological theory. Walter Cannon had various issues with the James-Lange theory of emotion. To begin, he contended that one can have the physical responses associated with emotional states without actually experiencing such states. If you have been exercising, for instance, the reason your heart rate is elevated is likely not fear.2
Also Read: Unforgettable Activities to Experience in Goa: Prices and Locations
Schachter-Singer Theory
The Schachter-Singer hypothesis is an example of a cognitive explanation of emotion; it is also known as the “two-factor theory of emotion.” According to this view, an individual’s physiological state must first become aroused before they can recognise the resulting feeling as an emotion. An emotion is the result of a stimulus triggering a physiological response, which is subsequently evaluated and labelled by the brain.4
Cognitive Appraisal Theory
This theory proposes that one experiences a stimulus, then has a thought, and then has a physiological response and an emotion at the same time. A bear sighting in the woods, for instance, could lead a person to fear for their safety. This sets up the body’s “fight or flight” reaction, accompanied by the unpleasant emotions of fear.5
Facial-Feedback Theory of Emotion
According to the facial-feedback idea, one’s emotional state can be gleaned from observing one’s own facial expressions. Early thinkers like Charles Darwin and William James recognised that physiological reactions might influence emotions directly rather than merely being a result of them.